Light
The light settings control the appearance of directional lighting used to illuminate 3D features such as columns and extruded polygons on the map.
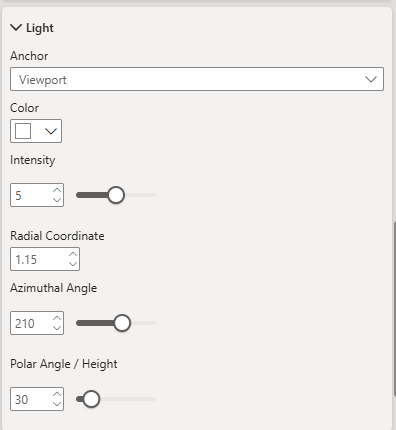
Lighting affects how shadows, highlights, and depth are perceived, especially when viewing pitched maps or 3D terrain. Adjusting these settings can enhance visual realism and help emphasise topographic detail.
Anchor
Determines whether the light source is fixed relative to the map's north or the viewport.
- Map – Light direction remains fixed relative to the map's north, rotating with the map.
- Viewport – Light direction stays fixed relative to the viewport, even when the map is rotated.
Color
Specifies the color of the light source. This can subtly tint highlights and shadows to create different visual effects.
Intensity
Controls the brightness of the light source. Higher values produce stronger highlights and deeper shadows.
Radial Coordinate
Adjusts the distance of the light source from the map's centre in radial units. A higher value positions the light further away, altering the softness of the illumination.
Azimuthal Angle
Sets the horizontal direction of the light source, measured in degrees.
- 0° points north, increasing clockwise.
For example, 90° is east, 180° is south, and 270° is west.
Polar Angle / Height
Determines the vertical angle of the light source above the horizon, measured in degrees. Lower values simulate sunrise/sunset lighting with longer shadows, while higher values create midday-style illumination with shorter shadows.